Human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet

A study led by an NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre scientist has identified, for the first time, how the human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR). Dr Nathan Hawkshaw is the lead author of a research paper published in Clinical & Translational Immunology, an open access, peer-reviewed journal.

Solar UV radiation reduces the barrier function of human skin

4‐phenylpyridine suppresses UVB‐induced skin inflammation by targeting c‐Src in vitro and in vivo - Kim - 2022 - Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine - Wiley Online Library

Transglutaminase 2 mediates UV-induced skin inflammation by enhancing inflammatory cytokine production
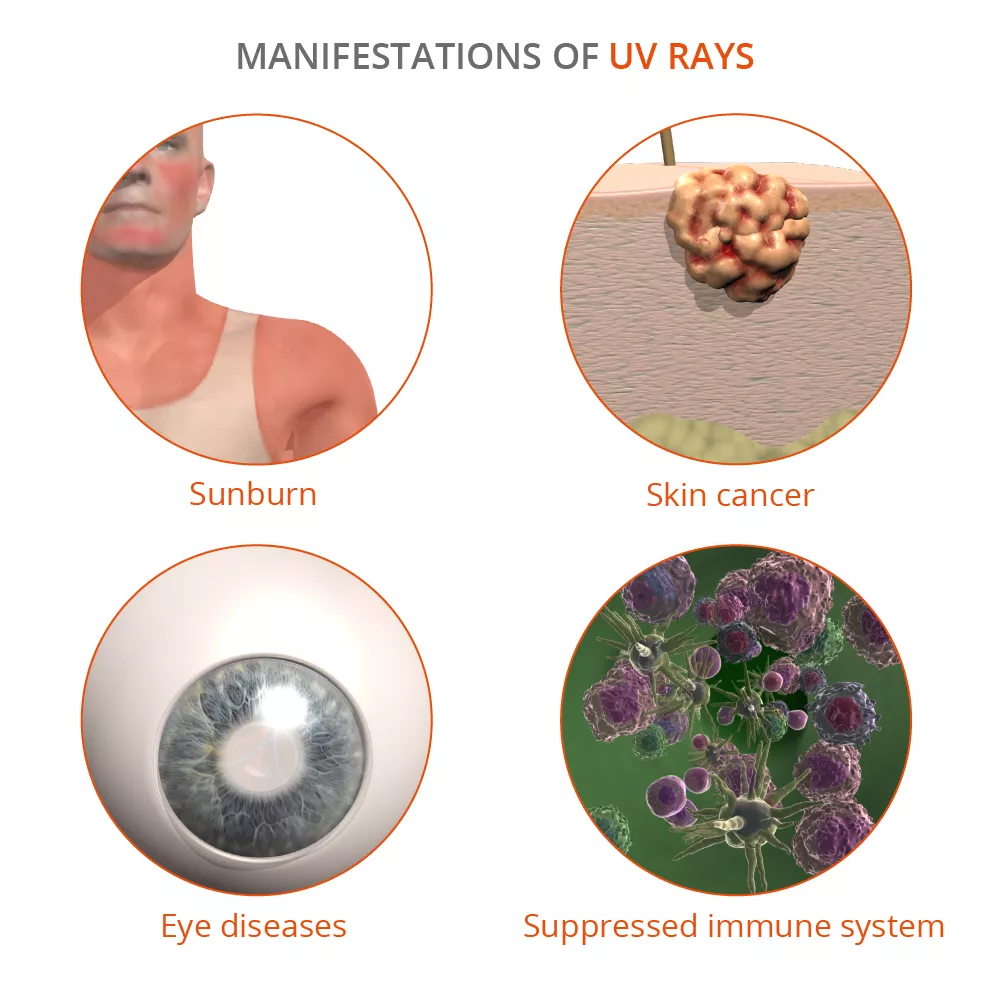
How the sun affects our anatomy and physiology

photobiology - Research & Innovation

GSDME deficiency leads to the aggravation of UVB-induced skin inflammation through enhancing recruitment and activation of neutrophils
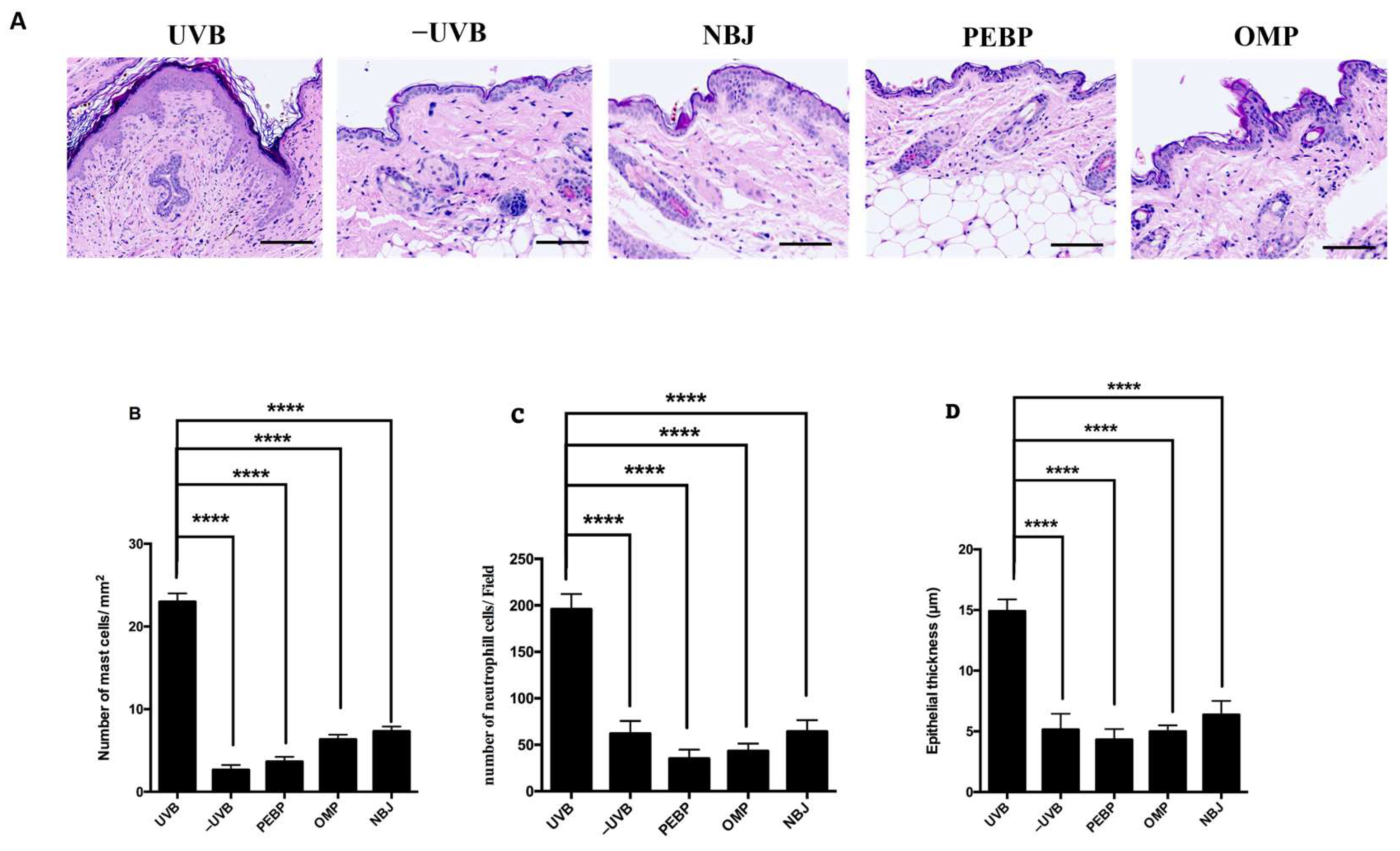
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text
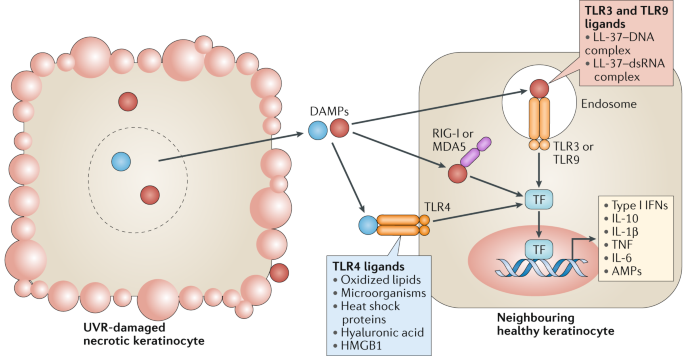
Photoimmunology: how ultraviolet radiation affects the immune system

Acute skin exposure to ultraviolet light triggers neutrophil-mediated kidney inflammation

Solar UV radiation reduces the barrier function of human skin

Platelet-activating factor is crucial in psoralen and ultraviolet A-induced immune suppression, inflammation, and apoptosis.

Skin Microbiome Modulates the Effect of Ultraviolet Radiation on Cellular Response and Immune Function - ScienceDirect